EC2-Other Costs in AWS: A Quick Guide to Understanding Them

Amazon EC2 has always been one of the heavy hitters in modern cloud computing. But despite its formidable reputation, even seasoned cloud operators can find themselves scratching their heads at its pricing structure, especially when it comes to the cryptic “EC2-Other” category in their AWS bills and how to save.
Understanding what goes into this cost category is essential for keeping your cloud budget in check (and your sanity intact). So in this article, let’s demystify the EC2-Other category to provide you with a better grasp of your overall EC2 costs.
Understanding EC2 Pricing
Before trying to understand the EC2-Other category, let’s start with a high-level overview of EC2 pricing.
Amazon EC2 is all about instances. So, most of your costs will come from instance usage. This primarily boils down to factors like instance type, amount of traffic, and region.
Apart from instance usage, there are also costs associated with tenancy, like whether you’re using Shared Hosts or Dedicated Instances. And finally, there’s costs related to payment options, like On-Demand, Reserved instances, or Spot Instances.
For the average AWS EC2 user, these costs make up pretty much all of their EC2 costs. However, nothing we’ve talked about so far fits under the mysterious EC2-Other category just yet.
What are EC2-Other Costs?
EC2-Other costs refer to anything and everything outside of the “big three” factors in instance usage, tenancy, and payment options. It encompasses various additional services or features associated with EC2 instances that aren’t covered in the usage, tenancy, and payment options.
Let’s look at the EC2 On-Demand Pricing page for some more direction on what that means. In the left navigation menu of this page, every header apart from “On-Demand Pricing” can qualify as an EC2-Other cost:

(The screenshot leaves out the bottom two since these are unlikely to show up in your bill.)
Specifically, let’s look at five categories that will likely make up the majority of your EC2-Other spending:
- Data Transfers
- Elastic Block Store (EBS) Volumes
- VPC-Related Charges: NAT Gateways & Elastic IP Addresses
- Load Balancing
- Auto Scaling
Data Transfers
Certain data transfers in and out of EC2 instances incur costs. Some examples of data transfer costs that you might be billed for include the following:
- Transfers between instances in different AWS Regions (i.e. to synchronize data between two instances)
- Transfers between an instance and another AWS service (i.e. an instance sends data to S3 storage)
- Transfers over the internet (i.e. sending data to clients accessing a web application hosted on an instance)
Exactly how much you’ll be charged depends on many factors, including how much data you transfer, and the specific start and destination Regions. Consider referring to our Ultimate Guide to AWS Data Transfer Pricing to understand the lower-level pricing details.
Elastic Block Store (EBS) Volumes
EBS volume costs pertain to charges associated with using block-level storage volumes for your EC2 instances. If you want your instances to have persistent storage, EBS is your solution.
AWS prices EBS volumes depending on volume type (i.e. gp2 vs. gp3, io1, or st1), allocation of storage capacity, and IOPS. Visit the Amazon EBS Pricing page for pricing details.
VPC-Related Charges: NAT Gateways & Elastic IP Addresses
When you launch an EC2 instance, you typically do so within an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Thus, charges for setting up NAT Gateways or Elastic IP Addresses, which are technically features that fall under the VPC umbrella, can show up as EC2-Other costs as well.
NAT Gateways essentially allow an EC2 instance within a private subnet to access the public internet, while not exposing the private IP address of the instance.
Elastic IP addresses are static IPv4 addresses that you can associate to your instances. Their main use is to allow you to easily reassign a stable and predictable IP address between your instances without requiring DNS updates.
Elastic IP addresses are considered “in-use” when associated with a running instance. They’re considered “idle” associated with a stopped instance, or not associated with any instances. AWS charges for both in-use and idle elastic IP addresses. Find more details on the Amazon VPC Pricing page.
Load Balancing
Load balancing costs in EC2 refer to charges associated with using Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) to distribute incoming traffic across multiple EC2 instances.
ELB offers several load balancing types, which affects pricing as well. These types include the Application Load Balancer (ALB) and Network Load Balancer (NLB). Specific pricing details can be found on the Elastic Load Balancing Pricing page.
Auto Scaling
Last but not least, auto scaling costs are associated with using AWS Auto Scaling to automatically manage the number of EC2 instances in your application based on demand or other predefined conditions. It’s a useful service to configure if your application sees varying traffic patterns over time.
Using AWS Auto Scaling itself does not incur any additional charges. However, you are billed for the instances launched by your Auto Scaling groups, along with associated charges like Amazon Cloudwatch costs for instance monitoring.
How Can I View My EC2-Other Costs in AWS Explorer?
If you’re an avid EC2 user, chances are you use some or all of these additional features. Finding out exactly how much AWS has been charging you to use them is actually very easy to do using AWS Cost Explorer.
AWS Cost Explorer lives in the AWS Billing and AWS Cost Management console, so let’s get there first. Follow these steps:
- Log in to your AWS Management Console.
- In the search bar at the top, type “Billing”. Choose Billing and Cost Management under Services. This takes you to the Billing and Cost Management console.
- Look for the Cost breakdown widget. If EC2-Other makes up a significant portion of your monthly spend, you can get a quick overview of how much you’re spending on it each month.
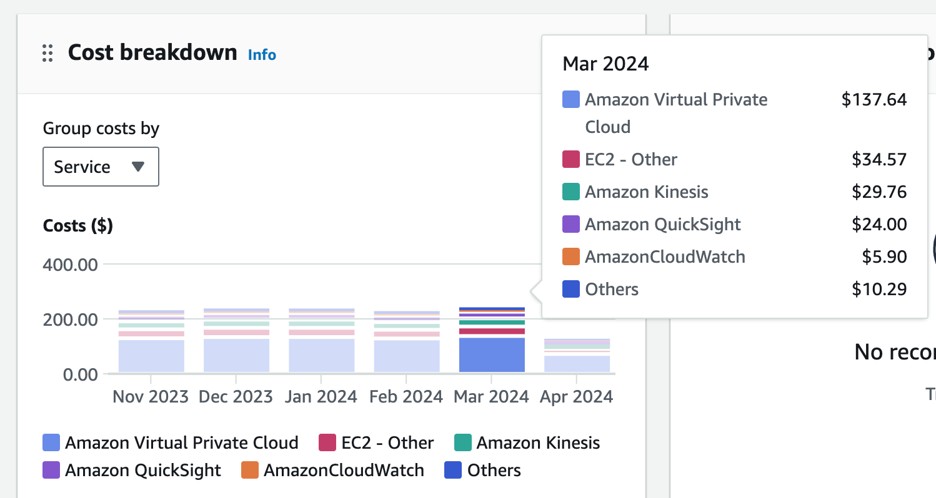
This is a nice overview, but it’d be even nicer to get a detailed breakdown of the EC2-Other category. To do that, we need to go into Cost Explorer proper. Follow these steps:
- From the Billing and Cost Management console, choose Cost Explorer in the left navigation menu.
- You’ll see a breakdown of all of your AWS costs. To narrow this down to EC2-Other costs only, apply the following filters in the right-hand menu:
- Group by – Usage type
- Service – EC2-Other
- Examine the resulting graph. This breaks down your EC2-Other costs into specific categories:
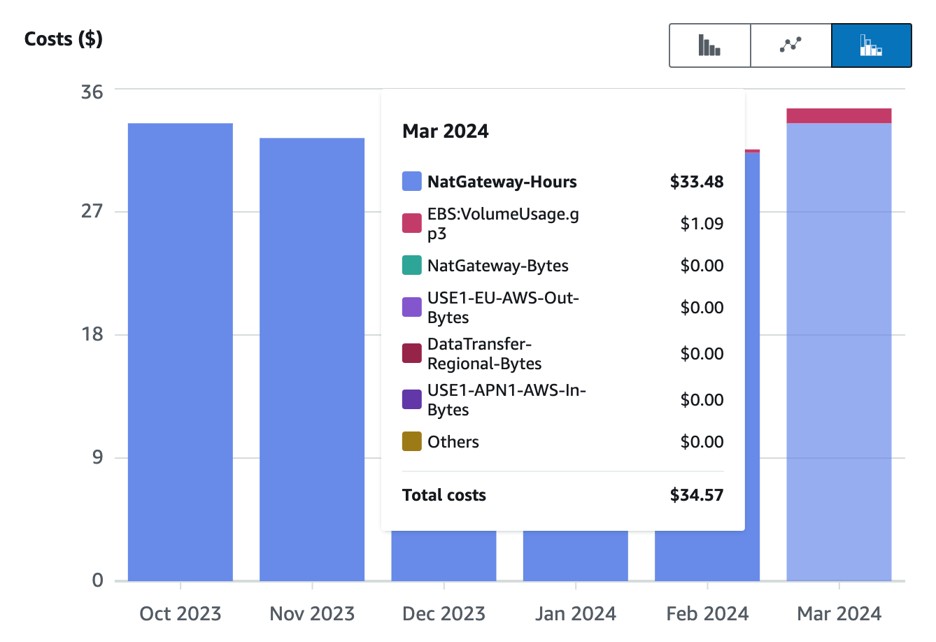
In this example, our EC2-Other costs come from NAT Gateway and EBS volume usage.
Conclusion
Bid farewell to the days of treating EC2-Other costs like a mysterious and unexpected expense. By understanding the additional charges associated with features like data transfers, EBS volumes, VPC-related services, load balancing, and auto-scaling, you can more effectively optimize your EC2 spending.
Moreover, we saw how easy it was to get a visual breakdown of all these costs in AWS Cost Explorer. This AWS tool is completely free for you to use, so start taking advantage of it today.
Manage, track, and report your AWS spending in seconds — not hours
CloudForecast’s focused daily AWS cost monitoring reports to help busy engineering teams understand their AWS costs, rapidly respond to any overspends, and promote opportunities to save costs.
Monitor & Manage AWS Cost in Seconds — Not Hours
CloudForecast makes the tedious work of AWS cost monitoring less tedious.
AWS cost management is easy with CloudForecast
We would love to learn more about the problems you are facing around AWS cost. Connect with us directly and we’ll schedule a time to chat!